Introduction
When it comes to treating coronary heart disease, patients often face a choice between two primary procedures: coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stent placement. This decision can be overwhelming and lead to apprehension. Understanding the differences, benefits, and risks associated with each procedure is essential for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. In this blog post, we will explore CABG and stent placement, addressing common patient apprehensions along the way.
CABG: The Traditional Approach
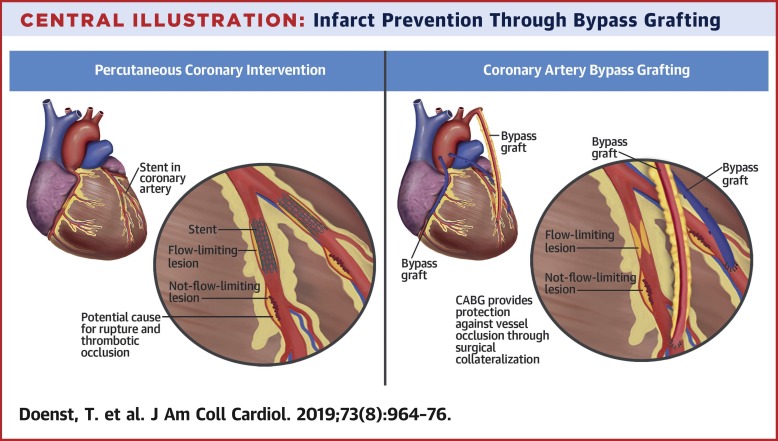
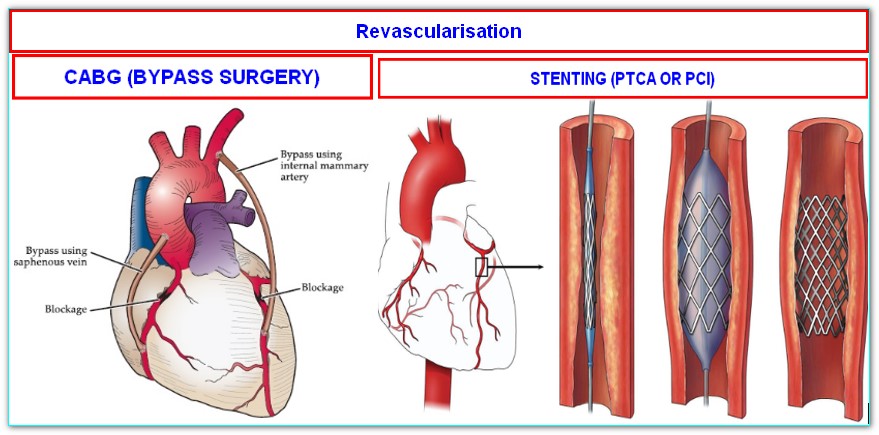
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), also known as heart bypass surgery, has been performed since the 1960s. It involves creating new pathways for blood to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, improving blood flow to the heart. During the procedure, a surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel, often from the patient’s leg or chest, and attaches it to the blocked artery, bypassing the problematic area. CABG is typically performed under general anesthesia and requires a hospital stay of about a week.
Stent Placement: A Minimally Invasive Option
2 . Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stent placement, commonly referred to as angioplasty, is a less invasive procedure compared to CABG. It involves inserting a catheter with a deflated balloon into the blocked artery, inflating the balloon to widen the artery, and then placing a stent to keep it open. A stent is a small mesh tube that provides support and prevents the artery from narrowing again. PCI with stent placement is usually performed under local anesthesia, and patients often go home the same day or the next day.
Addressing Patient’s Apprehensions:
- Recovery Time
One common apprehension among patients is the recovery time associated with each procedure. CABG generally requires a longer recovery period compared to stent placement. After CABG, patients may need to spend several days in the hospital and a few weeks at home before resuming normal activities. On the other hand, stent placement has a quicker recovery time, allowing patients to return to their daily routines sooner. However, it’s important to note that the recovery time can vary depending on individual circumstances, and it’s best to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
- Suitability for Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
Patients often wonder which procedure is suitable for their specific condition. Generally, CABG is recommended for patients with complex coronary artery disease, including those with multiple blockages or significant disease in the left main artery. Additionally, patients with diabetes may benefit more from CABG in terms of long-term survival outcomes. On the other hand, stent placement is often suitable for patients with less severe coronary artery disease or those who are not suitable candidates for CABG.
- Risks and Complications
Understanding the risks and potential complications associated with each procedure is crucial for addressing patient apprehensions. CABG is a major surgery, and like any surgical procedure, it carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Stent placement, although less invasive, also has its risks, including the possibility of stent thrombosis (clotting), restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery), and bleeding at the puncture site. It is important to note that healthcare professionals will thoroughly assess patients’ conditions and discuss potential risks before recommending a specific procedure.
- Long-Term Outcomes
Patients often have concerns about the long-term outcomes and effectiveness of the chosen procedure. Multiple studies have compared the long-term outcomes of CABG and stent placement. While both procedures have shown positive results in improving blood flow and relieving symptoms, long-term studies suggest that CABG may provide better outcomes in terms of survival, particularly for certain patient groups. However, individual patient factors, such as overall health, comorbidities, and the extent of coronary artery disease, should be considered when evaluating the expected outcomes.
Conclusion
Choosing between CABG and stent placement can be a daunting decision for patients. By understanding the differences, benefits, and risks associated with each procedure, patients can make informed decisions and address their apprehensions. Patients must have open and honest discussions with their healthcare professionals to ensure personalized care and the best possible outcomes.